Comparison of differential pressure method and pressure change method (pressure decay method)
The pressure change method (pressure decay method) directly displays the amount of pressure drop as the change in the pressure sensor output after the pressure is charged.
Scroll
| Differential pressure method | Pressure change method(Pressure decay method) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity |
|
|
| Temperature |
|
|
| Effects of temperature and deformation |
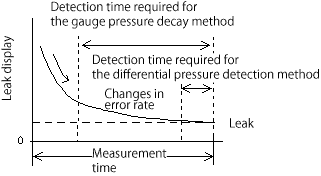 The initial stage of Pressurization includes many pressure fluctuations (errors) due to the effects of adiabatic and volume changes.
|
|
| Compatibility |
|
|